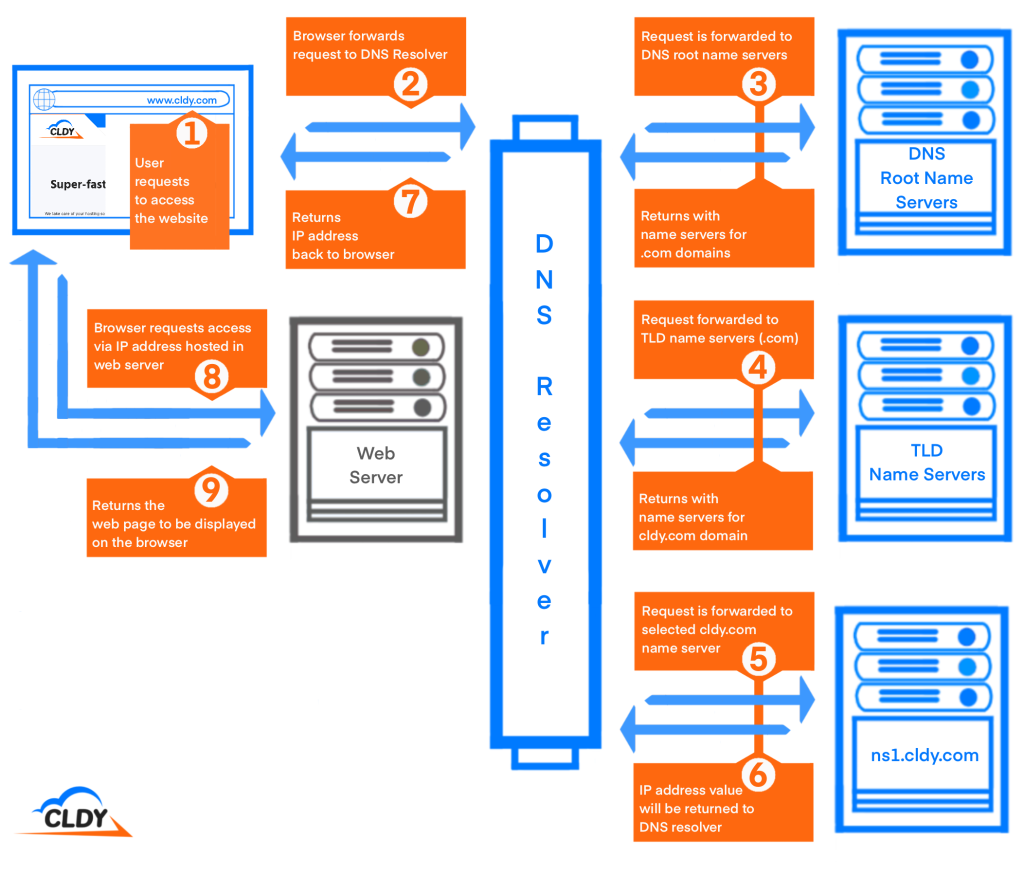
To know more about how DNS functions, check out the steps that the system follows from the user typing in the website in the browser’s address bar, to returning the web page to the user’s screen:
- The user enters the web site into the browser (e.g. www.cldy.com).
- This will be taken by the browser as a request to access the said website, and will have this request forwarded to a DNS resolver.
- The DNS resolver then forwards this to a DNS root name server. In return, this will provide the TLD name servers for .com domains (or depending on the domain suffix: .sg / .net / .org).
- DNS resolver forwards another request to the TLD name servers. This time, to return with the name servers associated with the cldy.com domain.
- The DNS resolver chooses a single name server, which will receive the request.
- The name server will now get the IP address value to return to the DNS resolver.
- The DNS resolver returns the IP address back to the browser.
(This IP address is also stored by the DNS resolver for some time, to make the process of accessing the website in the future much faster.) - The browser sends the request to access cldy.com to the web server which houses the website’s IP address. The web server will then determine the correct web page that should be displayed (e.g. homepage of cldy.com).
- The web server will now return the web page for www.cldy.com to the web browser, which will be displayed for the user.